Osteochondrosis of the neck is a common disease of the spine that affects patients of all ages.
It represents degenerative changes in the vertebral disc, developing against a background of severe stress, wearing the wrong shoes, heavy physical exertion, and malnutrition. It develops gradually, so the patient may not notice the first symptoms immediately.
The main signs of the disease
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis appear as the pathology progresses. They are more noticeable during an exacerbation. Having noticed the first signs of the disease, it is recommended to consult a doctor, as it is often disguised as other disorders, which complicates timely diagnosis.
Patients usually contact with the following complaints:
- Severe pain in the collar area.
- Noise and stuffiness in ears.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Shortness of breath, feeling of shortness of breath.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Blood pressure drops.
- Frequent fainting or syncope.
- Increase in body temperature.
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis in men do not differ much from those that appear in women. Patients complain of discomfort in the occiput, sternum, and shoulder girdle. You should contact your local therapist or neurologist for diagnosis.
Neck pain syndrome
One of the most common symptoms of chondrosis of the cervical spine is neck pain affecting the back of the head and shoulders. The nature of the pain (aching, sharp, light tingling) directly depends on the location of the lesion and the severity of the development of the pathological process. At the initial stage, this may be mild discomfort, which does not allow you to freely turn your head in all directions. Gradually, the pain becomes chronic and limits the range of motion.
Pain manifests itself as a result of deformation of the vertebrae, due to insufficient blood supply to the collar zone. Against the background of this process, spasms, attacks of anxiety and panic are observed. A painful sensation in the neck area can radiate to the shoulders or arms. Increase after sleep, sudden movements, laughing or sneezing. Discomfort is combined with a characteristic crunch when trying to turn or muscle weakness.
Spasm of muscle tissue and poor circulation often leads not only to pain, but also to temporary loss of the ability to move the neck. Constant overstrain spreads throughout the head, and the patient begins to complain of migraine attacks.
Tinnitus and stuffy ears
Osteochondrosis in the neck area is also manifested by a feeling of stuffiness in the ears, hearing loss, and noise. All this is due to insufficient intensity of blood flow to the vestibular apparatus. This complex of symptoms is called cochlear, but doctors rarely associate it with a disorder in the vertebral region. Pay attention to the nature of the noise and ringing in the ears, they usually intensify when a person is in one position for a long time or tries to change it.
Patients with hearing problems are referred to an otolaryngologist. In the presence of concomitant disorders of the condition, such as numbness of the face, limited mobility of the neck, additional consultation with a neurologist is required to clarify the diagnosis and determine the cause.
Headache and migraines
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men are rarely accompanied by frequent headaches, the female population is more susceptible to them. The vertebrae in this area are constantly exposed to excessive stress, which leads to their gradual deformation, if the muscle tissue is not elastic enough to keep them in a natural position. It is more difficult to identify the cause of the pain in the head, since the symptom is not specific.
The following reasons provoke an attack:
- Spasm of cerebral vessels.
- Pinched nerve endings in the cervicothoracic spine.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Acute violation of venous outflow.
- Increased fatigue.
- Prolonged stay in an unnatural position.
Headache aggravates during an exacerbation, and in a patient, including a male. By nature, it can be constant, dull in the form of seizures or pulsating. In older people, this symptom requires close attention, since it can speak of an incipient stroke, angina pectoris, heart attack or arterial hypertension. Therefore, first of all, these conditions are excluded before starting treatment for osteochondrosis.
With heart pathologies, patients also complain of compression in the chest area, an irregular heart rhythm, which allows the doctor to differentiate the condition in time. Headaches accompanied by nausea, shortness of breath, necessarily require an ECG.
Dizziness
Impaired coordination and frequent dizziness often appear when osteochondrosis develops to grade 2 or more. This is due to degenerative changes in the vertebrae, spasms, pinched nerve endings. The brain does not receive the required amount of oxygen, which negatively affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
As a result of the deviation of the state, the symptom is:
- Systemic vertigo.They appear as a sensation of the whole body and surrounding objects spinning. Dysfunction appears due to malfunction of the vestibular apparatus, weakening of muscle tissue and receptors located in the joints.
- Non-systemic vertigo.In addition to instability, patients experience bouts of nausea, an uncertain state in an upright position. Circular rotation is usually absent.
Dizziness is a serious symptom that should be treated immediately to a doctor. In the presence of numbness in the shoulders, paralysis of the muscle tissue of the face, loss of consciousness, emergency hospitalization is required.
Shortness of breath and lack of air
Another serious symptom of advanced osteochondrosis in the shoulder area is a constant feeling of lack of air. Breathing problems arise from compression of nerve endings and receptors that do not transmit impulses from the pharynx to the esophagus. Shortness of breath appears when the vertebrae are displaced, it increases in a stressful state, accompanied by a lump in the throat. After taking a sedative, the state of health returns to normal.
Lack of air provokes radicular syndrome. Spasm of the diaphragm affects the depth and rhythm of breathing. The patient becomes stuffy and hard to breathe air, problems with memory and concentration appear. Such a symptom in osteochondrosis requires immediate assistance, as it can cause a number of serious complications. The doctor selects the medicine individually, taking into account the condition.
Nausea
There is a large collection of nerve endings in the cervical region, where an artery runs, which is responsible for transporting nutrients to the brain. With osteochondrosis, protrusions and intervertebral hernias gradually form, which affects blood pressure, and as a result, the patient feels an attack of nausea.
Prolonged impairment of normal circulation leads to vomiting, loss of consciousness, and causes stroke and disability. Therefore, the appearance of such a symptom, not associated with nutritional errors, requires immediate medical advice.
Increased blood pressure
For cervical osteochondrosis, a typical symptom is a pressure jump during the day. For a long time, increased or decreased blood pressure is not maintained, which is a characteristic sign of degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc. The daily dynamics of blood pressure is spasmodic, since the irritation of the nerve endings is reflex and causes short-term spasms of the blood vessels.
A distinctive feature of increased pressure in cervical osteochondrosis is:
- headache;
- chest discomfort;
- decreased sensitivity in the collar zone;
- Muscle tension after being in one position for a long time.
All of this is taken into account when making a diagnosis. The rapid deterioration of the condition and sudden changes in pressure are the basis for hospitalization of the patient and providing him with assistance in a hospital setting.
Visual impairment
Osteochondrosis in the cervical spine often provokes such unpleasant symptoms as double vision, flickering, and the appearance of "flies". This signals the severity of the process, and requires a visit to a doctor.
Against the background of the destruction of connective tissue in the vertebrae, the following diseases can develop:
- Glaucoma.The patient is diagnosed with increased intraocular pressure, damage to the optic nerve. It is impossible to eliminate pathologists completely, only to achieve stable remission with complex treatment.
- Cataract.This pathological process leads to the destruction of the lens. The changes are associated with metabolic processes and acute disruption of oxygen supply to the brain. The first sign of the disease is the appearance of "flies" before the eyes. Timely start of treatment helps preserve the patient's vision.
- Claude Bernard-Horner's disease.Hypoxia in the occipital region is considered one of the causes of the lesion. The main signs of a pathological condition are a decrease in the reaction of the pupil or a difference in the size of the pupil in different eyes. Some patients complain that they cannot completely close their eyes for a night's rest, and twilight vision also suffers.
The ophthalmologist prescribes treatment after a thorough examination. But therapy is carried out only in a complex aimed at eliminating the cause of the violation. Only then can the problem be effectively dealt with.
Pharyngeal problems
Degenerative changes in the cervical vertebra provoke problems with swallowing. The patient complains of a lump in the throat, perspiration, sensation of a foreign body in the throat, itching. Signs indicate a malfunction of the neurovascular trunks that go from the spinal cord. But the symptomatology is not considered characteristic, and can be observed with pathological disorders such as inflammation, swelling.
Change in body temperature
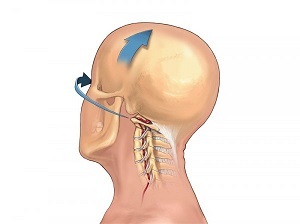
Osteochondrosis, as it progresses, causes an increase in body temperature. This symptomatology occurs when the vertebral artery is damaged, spinal canal stenosis or disc protrusion. It provokes changes in neurosis and concomitant neurological disorders.
Against the background of an increase in temperature, numbness of the tongue or hands, inflammation in the lymph nodes, burning of the tongue are observed.
The characteristic crunch when turning the neck allows osteochondrosis to be suspected.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis depending on the stage
Signs of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine largely depend on the stage of development of the pathology, the force of compression of the nerve endings and the process of disc deformation. It provokes the appearance of symptoms of compression of the vertebral artery and a violation of the flow of blood to the brain. Pinched nerve endings lead to severe neurological pathologies.
The severity of signs directly depends on the stage of development of the disease:
- Initial.The degenerative processes in the vertebral discs proceed unnoticed by the patient. It is quite difficult to notice the first changes, since these can be mild headaches (more felt in women), discomfort in the neck, slight deterioration in vision or loss of sensitivity in the collar zone. At this stage, patients rarely go to the doctor, attributing the symptoms to fatigue, lack of sleep or stress.
- Second stage.As the pathology progresses and disc protrusion appears, more pronounced symptoms appear. The destruction of the annulus fibrosus affects the movements of the head, they become more limited. Also, patients begin to complain of constant ringing in the ears, impaired visual function, pain in the neck with a characteristic crunch, problems with swallowing, sleep disturbance, and decreased clarity of reflexes. Keeping the head in one position causes extreme discomfort, which requires a doctor's consultation.
- Third stage.Gradually, intervertebral hernias are formed, the fibrous ring is completely destroyed, there is deformation of the vertebrae, displacement of bone segments, dislocations, instability. The patient complains of acute pain in the neck, pronounced shoulder syndrome, paralysis of the upper limbs, tendon reflexes are not observed, impaired sensitivity in the scalp. This is a severe stage of the disease that requires complex treatment.
Osteochondrosis is a chronic systemic disease that manifests itself in various symptoms. The reason is always hidden in the compressed nerve endings, circulatory disorders and deformation of the intervertebral discs. Protrusion, hernia and displacement gradually lead to loss of mobility of the vertebra.
Age directly affects the severity of symptoms. The older the patient, the stronger the changes in the connective and bone tissues. This is due to muscle fiber weakness, nutritional deficiencies, and chronic inflammatory diseases in the body.
Patient Reviews
Osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae is a common disease, since the nerve roots are constantly exposed to stress due to excessive mobility of the segment. Timely detection of pathology avoids serious complications, so many people read patient reviews and compare them with their symptoms.
It is strictly forbidden to diagnose yourself without laboratory and apparatus tests. Any information should only be taken as a note.
Cervical osteochondrosis is manifested by a large number of symptoms, but most of them are easily confused with similar pathologies. Therefore, it is recommended to consider the patient's complaints in a complex and carry out differential diagnostics, which allows to timely identify the disease and prescribe the correct treatment, which includes physiotherapy, gymnastics and drug treatment.












































